Abstract
Despite recent emergence of novel target agents, allogeneic stem cell transplantation is still the favored option for disease control in relapsed patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Allotransplant from alternative donors such as haploidentical donor or cord blood can be done when fully HLA matched donor is not available. As for patients relapsed after the first stem cell transplantation (SCT1), these alternative stem cell sources often become only available options for the second transplantation. However, there has been no report comparing haploidentical stem cell (HIT) and cord blood transplantation (CBT), especially for the second transplantation.
We performed a retrospective cohort study on AML patients who relapsed after SCT1 and underwent second allogeneic SCT from either alternative donor at our institution. We identified a total of 50 corresponding patients between January 2008 and February 2021 where 31 HIT and 19 CBT were included, and analyzed SCT outcomes including overall survival (OS), disease free survival (DFS), cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), non-relapse mortality (NRM) and the incidence of SCT complications with comparing between the 2 groups. Conditioning regimens for HIT and for CBT were as follows: Fludarabine (30mg/m2/day intravenous (IV) for 5 days), busulfan (3.2mg/kg/day IV for 2 days), fractionated total body irradiation (fTBI, 4-8Gy total) and rabbit antithymoglobulin at a dose of 1.25mg/kg/day for four days for in vivo T cell depletion from D-5 to D-2 was given for HIT. G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood stem cell was used as allograft. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis was done with tacrolimus and methotrexate. For CBT, fludarabine (30mg/m2/day IV for 5 days), cytarabine (1.5g/m2 twice daily for 3 days) with fTBI (12Gy). All CBT patients received double cord blood units. GVHD prophylaxis was done with tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil.
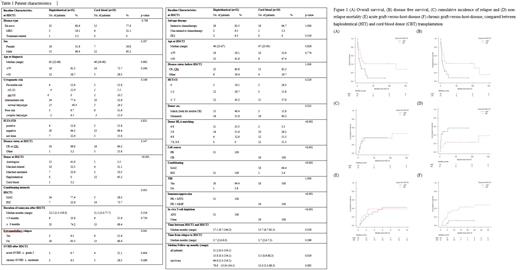
The median follow-up period for survivors was 64.6 months (range 5.3-154.1). The type of SCT1 differed between the two groups; more patients of HIT were the recipient of prior autologous transplantation (41.9%), and 63.2% of CBT had underwent prior HIT (p<0.001). However, age, sex, disease status pre-transplant, HCT-CI, time from SCT1 to relapse, time from post-transplant relapse to SCT2, FLT3-ITD mutation status and cytogenetic risk distribution did not differ between each group.
Overall respective outcomes of HIT and CBT were as follows; 41% and 29% for 2-year OS (p=0.017), 41% and 16% for 2-year DFS (p=0.016), 36% and 36% for 2-year CIR (p=0.91) and 23% and 48% for 2-year NRM (p=0.021). Early NRM within 100 days of SCT2 was more frequent in CBT than HIT although not statistically significant (26.3% vs 9.7%, p=0.23). Median days to neutrophil and platelet engraftment were 12 (range 11-23) and 13 (range 9-38) in HIT, and 29 (range 16-48), 51 (range 27-167) for CBT, respectively (p<0.001 for both). Cumulative incidence of acute and chronic GVHD were analyzed as follows; 39% and 42% for 1-year acute GVHD (p=0.82) and 43% and 11% for 2-year chronic GVHD (p=0.037) in HIT and CBT. In multivariate analysis, acute GVHD ≥ grade 2 after SCT1 (HR for OS 2.68, p=0.023; HR for DFS 2.49, p=0.036) and cytogenetic risk at diagnosis (HR for OS 2.07, p=0.018; HR for DFS 2.02, p=0.019) were significantly associated with worse outcomes. Hemorrhagic cystitis occurred more frequently in HIT patients than CBT group (32.3% vs 5.3%, p=0.035), while there were no significant differences between incidences of CMV DNAemia, CMV disease, thrombotic microangiopathy and sinusoidal obstructive syndrome. In subgroup analysis for patients relapsed after first allogeneic SCT1 only (18 patients in HIT and CBT group each), trend towards better outcomes in HIT than CBT were present, similar to those of all patients; 38% and 25% for 2-year OS (p=0.095), 39% and 10% for 2-year DFS (p=0.10), 22% and 51% for 2-year NRM (p=0.11) and 40% and 39% for 2-year CIR (p=0.90).
This is the first report, to the best of our knowledge, to compare outcomes of the second transplantation from alternative donors for relapsed AML patients after SCT1. Our unique T-cell replete HIT using a reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen seems to provide better survival than CBT.
Lee: Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kim: AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AIMS Biosciense: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; AML-Hub: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BL & H: Research Funding; BMS & Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Boryung Pharm Co.: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Handok: Consultancy, Honoraria; LG Chem: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pintherapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi Genzyme: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; SL VaxiGen: Consultancy, Honoraria; VigenCell: Consultancy, Honoraria.